表格
概述
简介
表格是一种常见的 UI 模式,用于在 Web 应用中显示记录列表。Filament 提供了一个基于 PHP 的 API,用于定义具有许多功能的表格,同时还具有令人难以置信的可定制性。
定义表格列
任何表格的基础都是行和列。Filament 使用 Eloquent 获取表中行的数据,而由你负责定义该行中使用的列字段。
Filament 包含许多预先构建的列类型,你可以在此处查看完整列表。你甚至可以创建自己的自定义列类型以所需的任何方式显示数据。
列存储在数组中,作为 $table->columns() 方法中的对象:
use Filament\Tables\Columns\IconColumn;
use Filament\Tables\Columns\TextColumn;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->columns([
TextColumn::make('title'),
TextColumn::make('slug'),
IconColumn::make('is_featured')
->boolean(),
]);
}

上例中,表格中有 3 列。前两列显示文本 - 表格中每行的标题及 slug。第三列显示图标,根据 is_featured 值是否为真显示为绿色勾选或者红色打叉图标,
让列可排序及可搜索
你可以通过将方法链式调用到列上来轻松修改列。例如,你可以使用 searchable() 方法将列设置为可搜索。现在,表中将有一个搜索字段,并且你可以根据该列的值过滤行:
use Filament\Tables\Columns\TextColumn;
TextColumn::make('title')
->searchable()

你可以使多个列可搜索,Filament 将能够一次性搜索其中任意一列的匹配项。
你还可以使用 sortable() 方法使某个列可排序。这将在列标题中添加一个排序按钮,点击该按钮即可按该列对表格进行排序:
use Filament\Tables\Columns\TextColumn;
TextColumn::make('title')
->sortable()

访问列中的关联数据
你也可以在列中展示关联数据。比如,你有一个属于 User 模型(作者)的 Post 模型,你可以在表格中展示用户名:
use Filament\Tables\Columns\TextColumn;
TextColumn::make('author.name')

这种情况下,Filament 将会在 Post 模型上搜索 author 关联,然后展示该关联的 name 属性。我们称之为“点语法”,你可以用它来展示任何关联的任何属性,甚至是嵌套关联。Filament 使用点语法来饥渴加载关联的结果。
更多有关列关联的信息,请查阅相关关联文档。
在现有列旁边添加新列
虽然 columns() 方法会重新定义表格的所有列,但有时你可能希望将列添加到现有配置中,而无需完全覆盖它。当你拥有需要跨多个表格显示的全局列配置时,这尤其有用。
Filament 为此提供了 pushColumns() 方法。与 columns() 替换整个列配置不同,pushColumns() 会将新列附加到任何现有列。
当与服务提供者(例如 AppServiceProvider)的 boot() 方法中的全局表设置结合使用时,此功能尤其强大:
use Filament\Tables\Columns\TextColumn;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
Table::configureUsing(function (Table $table) {
$table
->pushColumns([
TextColumn::make('created_at')
->label('Created')
->sortable()
->toggleable(isToggledHiddenByDefault: true),
TextColumn::make('updated_at')
->label('Updated')
->sortable()
->toggleable(isToggledHiddenByDefault: true),
]);
});
定义表格过滤器
除了将列设置为 searchable()(允许用户通过搜索列内容来过滤表格)之外,你还可以允许用户以其他方式过滤表格中的行。过滤器 可以在 $table->filters() 方法中定义:
use Filament\Tables\Filters\Filter;
use Filament\Tables\Filters\SelectFilter;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->columns([
// ...
])
->filters([
Filter::make('is_featured')
->query(fn (Builder $query) => $query->where('is_featured', true)),
SelectFilter::make('status')
->options([
'draft' => 'Draft',
'reviewing' => 'Reviewing',
'published' => 'Published',
]),
]);
}

此例中,我们定义了两个表格过滤器。表格顶部角落现在有一个“过滤器”图标按钮。点击它将打开一个下拉菜单,其中包含我们定义的两个过滤器。
第一个过滤器渲染成复选框。选中时,仅显示表格中的选中行。取消选中时,将显示所有行。
第二个过滤器渲染成选择下拉菜单。当用户选择一个选项时,仅显示具有该状态的行。当未选择任何选项时,将显示所有行。
你可以使用任何 Schema 组件来构建过滤器的用户界面。例如,你可以创建自定义日期范围过滤器。
定义表格操作
Filament 的表格可以使用 Action。这些按钮可以添加到任意表格行的末尾,甚至可以添加到表格的 header。例如,你可能希望在表头中“创建”一条新记录,然后在每行上执行“编辑”和“删除”操作。批量操作 可用于在选中表格中的记录时执行代码。
use App\Models\Post;
use Filament\Actions\Action;
use Filament\Actions\BulkActionGroup;
use Filament\Actions\DeleteBulkAction;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->columns([
// ...
])
->recordActions([
Action::make('feature')
->action(function (Post $record) {
$record->is_featured = true;
$record->save();
})
->hidden(fn (Post $record): bool => $record->is_featured),
Action::make('unfeature')
->action(function (Post $record) {
$record->is_featured = false;
$record->save();
})
->visible(fn (Post $record): bool => $record->is_featured),
])
->toolbarActions([
BulkActionGroup::make([
DeleteBulkAction::make(),
]),
]);
}

上例中,我们为表格行定义了两个操作。第一个操作是 “feature” 操作。点击后,它会将记录的 is_featured 属性设置为 true——该属性在action() 方法中写入。使用 hidden() 方法,如果记录已是 featured,则隐藏该操作。第二个操作是 “unfeature” 操作。点击后,它会将记录的 is_featured 属性设置为 false。使用 visible() 方法,如果记录不是 featured,则隐藏该操作。
我们还定义了一个批量操作。定义批量操作后,表格中的每一行都会有一个复选框。此批量操作内置于 Filament,它将删除所有选定的记录。当然,你也可以轻松编写自己的自定义批量操作。

Action 还可以打开模态框来请求用户确认,并在其中渲染表单以收集额外数据。建议你阅读 Actions 文档,以了解更多有关其在 Filament 中的丰富功能。
分页
】 Filament 表格默认进行分页。用户可以选择每页显示 5、10、25 或 50 条记录。如果记录数量超过所选数量,用户可以使用分页按钮在页面之间导航。
自定义分页选项
你可以通过将每页分页记录的选项传递给 paginated() 方法来自定义它们:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->paginated([10, 25, 50, 100, 'all']);
}
NOTE
请注意,使用非常大的数字和 all 时,大量记录可能会导致性能问题。
自定义默认分页页面选项
要自定义显示的默认记录数,请使用 defaultPaginationPageOption() 方法:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->defaultPaginationPageOption(25);
}
NOTE
请确保分页选项中包含默认分页选项。
显示链接到首页和最后一页的分页链接
使用 extremePaginationLinks() 方法向第一页和最后一页添加“端点(extreme)”链接:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->extremePaginationLinks();
}
使用简单分页
使用 paginationMode(PaginationMode::Simple) 方法,你可用使用简单分页:
use Filament\Tables\Enums\PaginationMode;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->paginationMode(PaginationMode::Simple);
}
使用 Cursor 分页
使用 paginationMode(PaginationMode::Cursor) 方法,你可以使用光标(cursor)分页:
use Filament\Tables\Enums\PaginationMode;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->paginationMode(PaginationMode::Cursor);
}
防止查询字符串与分页页面冲突
默认情况下,Livewire 将分页状态存储在 URL 查询字符串的 page 参数中。如果同一页面上有多个表格,则意味着一个表格的分页状态可能会被另一个表格的状态覆盖。
为了解决这个问题,你可以定义一个 $table->queryStringIdentifier(),为该表返回唯一的查询字符串标识符:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->queryStringIdentifier('users');
}
禁用分页
默认情况下,表格会分页显示。要禁用分页,请使用 $table->paginated(false) 方法:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->paginated(false);
}
记录 URL (可点击的行)
使用 $table->recordUrl() 方法,你可以让表格行整行都是可点击的:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->recordUrl(
fn (Model $record): string => route('posts.edit', ['record' => $record]),
);
}
当使用资源 表时,每行的 URL 通常已经为你设置好了,但可以调用此方法来覆盖每行的默认 URL。
TIP
你还可以重写特定列的 URL,或在点击某个列时触发操作。
你也可以在新的标签页中打开 URL:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->openRecordUrlInNewTab();
}
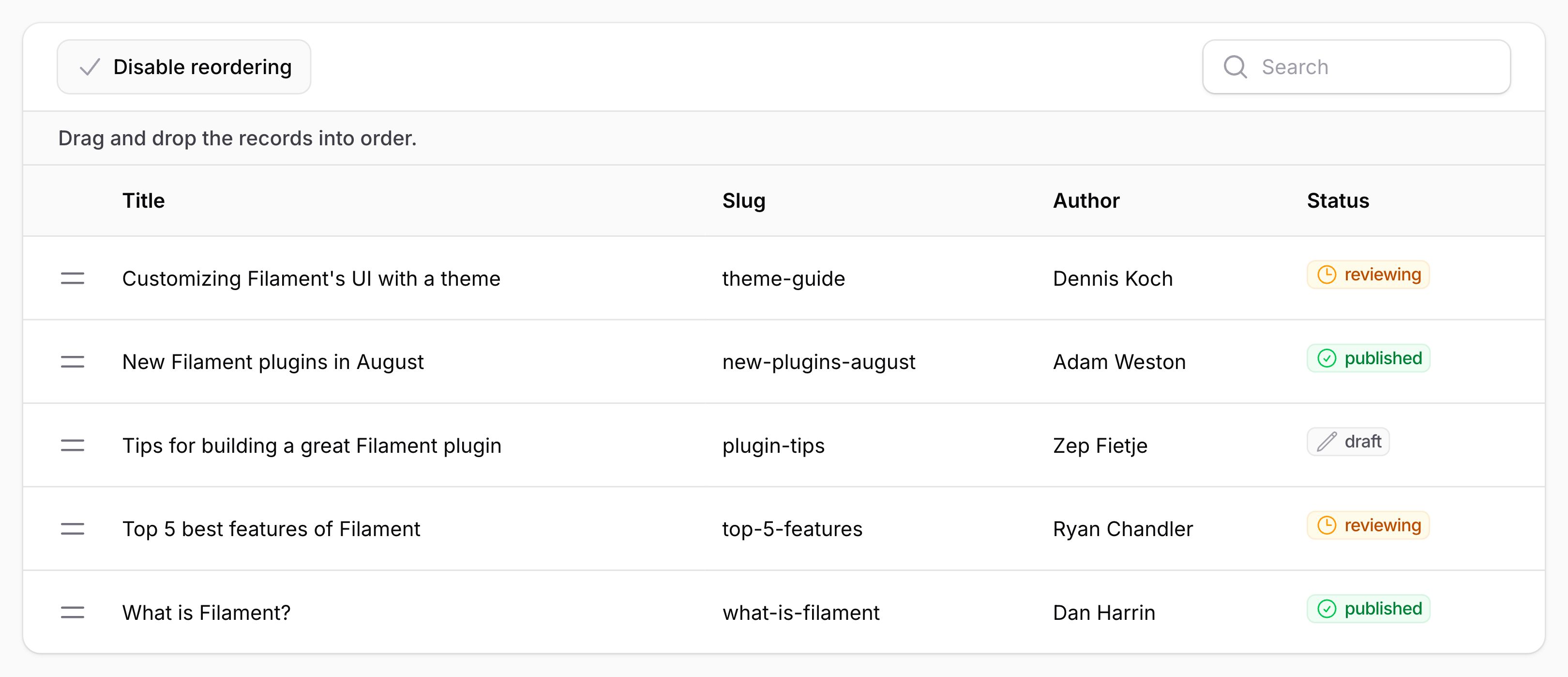
重新排序记录
使用 $table->reorderable() 方法,你可以允许用户在表格中使用拖拽对记录进行重新排序:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->reorderable('sort');
}
如果你在模型上使用批量赋值保护,你也需要将 sort 属性添加到 $fillable 数组中:
当表格可重新排序时,表格上将有一个新按钮用以切换重新排序。

reorderable() 方法接受一个列名用以保存记录的排序顺序。如果你使用了 spatie/eloquent-sortable,它的排序字段名为 order_column,那么你可以这样使用:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->reorderable('order_column');
}
reorderable() 方法也接受布尔值条件作为其第二个参数,允许你条件性地启用重新排序:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->reorderable('sort', auth()->user()->isAdmin());
}
重新排序时启用分页
在重新排序模式下,分页将被禁用,以允许你在页面之间移动记录。在重新排序时进行分页通常会有不好的体验,不过如果你想重写此功能,可以使用 $table->paginatedWhileReordering():
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->paginatedWhileReordering();
}
自定义重新排序的触发操作
要自定义重新排序的触发按钮,你可以使用 reorderRecordsTriggerAction() 方法,并传入一个返回 Action 的闭包。所有自定义 Action 触发按钮中可以使用的方法,都可以在此处使用:
use Filament\Actions\Action;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->reorderRecordsTriggerAction(
fn (Action $action, bool $isReordering) => $action
->button()
->label($isReordering ? 'Disable reordering' : 'Enable reordering'),
);
}
自定义表格标题
使用 $table->heading() 方法,你可以给表格添加标题:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->heading('Clients')
->columns([
// ...
]);
}
你也可以使用 $table->description() 方法,在标题下方添加描述:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->heading('Clients')
->description('Manage your clients here.')
->columns([
// ...
]);
}
你可以传递视图给 $table->header() 方法,自定义整个标题的 HTML:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->header(view('tables.header', [
'heading' => 'Clients',
]))
->columns([
// ...
]);
}
轮询表内容
使用 $table->poll() 方法,你可以轮询表格内容,使之在设置的时间间隔内刷新数据:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->poll('10s');
}
延迟加载
有大量数据的表格的加载可能需要一些时间,在这种情况下,你可以使用 deferLoading() 方法异步加载表格数据:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->deferLoading();
}
使用 Laravel Scout 搜索记录
虽然 Filament 没有提供与 Laravel Scout 直接交互的集成,你可以在 searchUsing() 方法中使用 whereKey() 子句去过滤用于 Scout 的查询:
use App\Models\Post;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->searchUsing(fn (Builder $query, string $search) => $query->whereKey(Post::search($search)->keys()));
}
正常情况下,Scout 内部使用 whereKey() (whereIn()) 方法来进行检索,因此,使用它不会带来性能损失。
为了显示全局搜索输入,表中至少有一列需要是 searchable()。或者,如果你使用 Scout 来控制哪些列已经可以搜索,你可以简单地将 searchable() 传递给整个表:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->searchable();
}
设置表格行样式
条纹状表格行
要让表格行启用斑马条纹,你可以使用 striped() 方法:
use Filament\Tables\Table;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->striped();
}

自定义行类
你可能希望基于记录数据条件性地设置行样式。使用 $table->recordClasses() 方法,将指定字符串或者 CSS 类数组应用到行中,可以实现此目的:
use App\Models\Post;
use Closure;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
public function table(Table $table): Table
{
return $table
->recordClasses(fn (Post $record) => match ($record->status) {
'draft' => 'draft-post-table-row',
'reviewing' => 'reviewing-post-table-row',
'published' => 'published-post-table-row',
default => null,
});
}
全局设置
要自定义所有表格的默认配置,你可以在服务提供者的 boot() 方法中调用其静态 configureUsing() 方法。该函数将在每次创建表格时运行:
use Filament\Tables\Enums\FiltersLayout;
use Filament\Tables\Table;
Table::configureUsing(function (Table $table): void {
$table
->reorderableColumns()
->filtersLayout(FiltersLayout::AboveContentCollapsible)
->paginationPageOptions([10, 25, 50]);
});
Still need help? Join our Discord community or open a GitHub discussion










